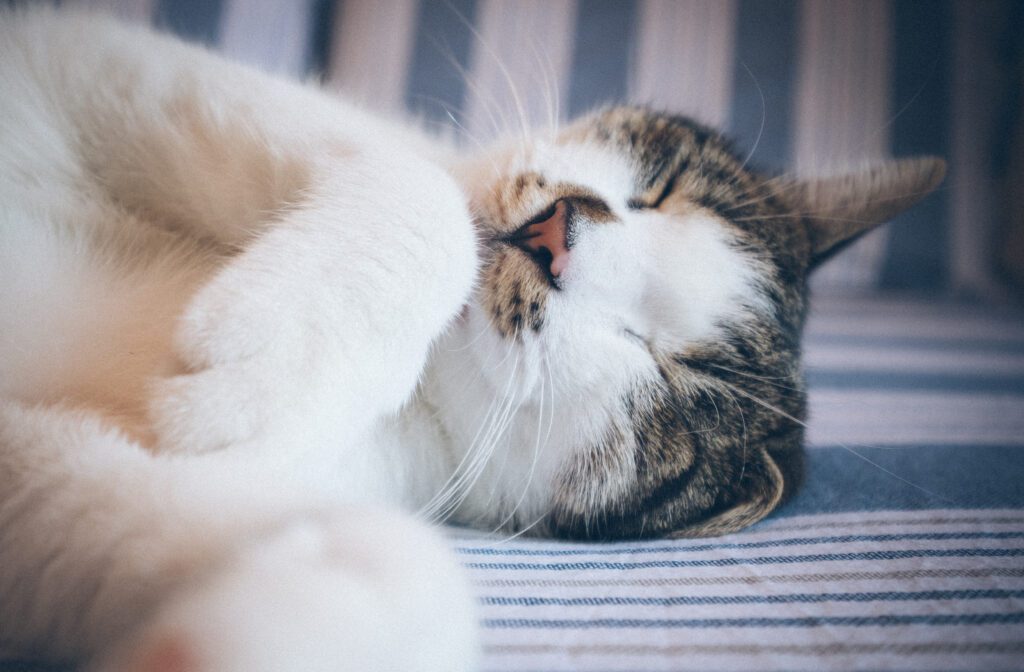
What causes babies to roll their eyes and breathe rapidly while sleeping?
Babies may roll their eyes and breathe rapidly during sleep for a variety of reasons. One common cause is the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, which is characterized by increased brain activity and vivid dreams. During REM sleep, babies may exhibit eye movements, including rolling or fluttering of the eyes. This is a normal part of the sleep cycle and does not typically indicate any health concerns.
Another possible cause of eye rolling and rapid breathing in babies during sleep is the occurrence of dreams or nightmares. Just like adults, babies can experience dreams during their sleep, which may lead to eye movements and changes in breathing patterns. These episodes are usually brief and do not require any intervention.
In some cases, eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep may be associated with gastroesophageal reflux (GER), a condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This can cause discomfort or pain for the baby, leading to restless sleep with eye rolling and rapid breathing as potential symptoms. If GER is suspected, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
At what age do babies typically start rolling their eyes and breathing rapidly during sleep?
Babies can start rolling their eyes and breathing rapidly during sleep from birth onwards. However, these behaviors are more commonly observed when babies reach around 3-4 months old. At this age, infants begin to have more developed neurological systems, including the ability to enter REM sleep cycles.
During the first few months of life, babies spend a significant amount of time in deep non-REM (NREM) sleep stages. As they mature, they gradually transition into lighter NREM stages and REM sleep cycles become more prominent. It is during these REM cycles that eye rolling and rapid breathing are most likely to occur.
It is important to note that every baby is unique, and the exact age at which they start exhibiting these behaviors may vary. Some babies may start earlier or later than others, and this is considered within the normal range of development.
Are there any potential health concerns associated with baby eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep?
In most cases, eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep are not indicative of any underlying health concerns in babies. As mentioned earlier, these behaviors are often a normal part of the sleep cycle and can be attributed to REM sleep or dreams.
However, if eye rolling and rapid breathing are accompanied by other worrisome symptoms such as choking, gasping for air, or prolonged periods of disrupted sleep, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. These signs could indicate an underlying medical condition such as sleep apnea or gastroesophageal reflux (GER), which may require further evaluation and treatment.
If parents have any concerns about their baby’s sleep patterns or notice any unusual changes in behavior during sleep, it is always best to seek guidance from a pediatrician or healthcare provider for appropriate assessment and reassurance.
How long does it usually last when a baby experiences eye rolling and rapid breathing while sleeping?
The duration of eye rolling and rapid breathing episodes during baby’s sleep can vary. In most cases, these episodes are relatively brief and last only a few seconds to a couple of minutes. They often occur sporadically throughout the night as the baby transitions between different stages of sleep.
During REM sleep cycles, which typically last around 20-30 minutes in infants, babies may experience multiple instances of eye rolling and rapid breathing. However, once the REM stage ends and the baby enters deeper NREM stages, these behaviors tend to subside.
If a baby is experiencing prolonged or frequent episodes of eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep that last for more than a few minutes at a time, it may be worth discussing with a healthcare professional to rule out any potential underlying issues.
Can environmental factors contribute to baby eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep?
Yes, environmental factors can sometimes contribute to baby eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep. Some common factors include:
Noise:
Loud or sudden noises in the environment can startle babies during their sleep, causing them to momentarily roll their eyes and exhibit rapid breathing. Ensuring a quiet and calm sleeping environment can help minimize these disturbances.
Temperature:
An uncomfortable temperature in the room can disrupt a baby’s sleep and lead to restless movements, including eye rolling. It is important to maintain an optimal temperature for the baby’s comfort, typically between 68-72°F (20-22°C).
Lighting:
Bright lights or excessive light exposure in the room can interfere with a baby’s ability to fall into deep sleep stages. Creating a dark and soothing sleeping environment can promote better quality sleep and reduce the likelihood of eye rolling.
Sleep position:
The position in which a baby sleeps can also impact their comfort level and potentially contribute to eye rolling. Ensuring that the baby is placed on their back for sleep, as recommended by pediatric experts, helps reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) while providing a safe sleeping position.
Is it normal for babies to exhibit other unusual behaviors, like twitching or jerking movements, along with eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep?
Yes, it is normal for babies to exhibit other unusual behaviors along with eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep. These behaviors can include twitching, jerking movements, or even brief muscle contractions.
These movements are often referred to as “sleep starts” or hypnagogic myoclonus and are considered a normal part of the sleep cycle. They typically occur during the transition between wakefulness and sleep or during sudden awakenings from deep sleep stages.
While these movements may appear alarming to parents, they are generally harmless and do not require any intervention. It is important to remember that babies’ neurological systems are still developing, and these movements reflect their immature nervous system rather than a sign of an underlying health issue.
Are there any recommended strategies to help soothe a baby who is experiencing eye rolling and rapid breathing while sleeping?
If a baby is experiencing eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep and appears restless or uncomfortable, there are several strategies that parents can try to soothe them:
Gentle touch or rocking:
Providing gentle touch or rhythmic rocking motions can help calm a baby’s nervous system and promote relaxation. This can be achieved through gentle pats on the back, rocking in a chair, or using a baby swing or vibrating bassinet.
White noise or soothing sounds:
Playing white noise or soothing sounds in the background can create a calming environment for the baby. The repetitive nature of these sounds can help drown out external noises and promote better quality sleep.
Adequate feeding before bedtime:
Ensuring that the baby has had a sufficient feeding before bedtime can help prevent hunger-related discomfort during sleep. A full stomach can contribute to better overall comfort and reduce the likelihood of restlessness.
Creating a consistent bedtime routine:
Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can signal to the baby that it is time to wind down and prepare for sleep. This can include activities such as a warm bath, gentle massage, reading a book, or singing a lullaby.
It is important to remember that every baby is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. It may require some trial and error to find the most effective soothing strategies for an individual baby.
Do certain medical conditions or medications increase the likelihood of baby eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep?
While eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep are often normal occurrences in babies, certain medical conditions or medications can increase the likelihood of these behaviors:
Sleep apnea:
Babies with sleep apnea may exhibit frequent pauses in breathing during their sleep. These pauses can lead to oxygen deprivation and potentially cause eye rolling and rapid breathing when they resume breathing. Sleep apnea in infants is relatively rare but should be evaluated by a healthcare professional if suspected.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER):
Babies with GER may experience acid reflux or regurgitation of stomach contents into the esophagus during sleep. This can cause discomfort or pain, leading to restless movements such as eye rolling and rapid breathing. If GER is suspected, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
Medications:
Certain medications prescribed to babies, such as those used for treating respiratory conditions or seizures, can have side effects that affect sleep patterns. These medications may alter brain activity during sleep, potentially leading to eye rolling and changes in breathing patterns. If parents have concerns about medication side effects, they should discuss them with the prescribing healthcare professional.
If parents suspect that a medical condition or medication may be contributing to their baby’s eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
What signs should parents look out for if they suspect something more serious than normal eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep in their baby?
While eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep are typically normal occurrences in babies, there are certain signs that parents should look out for if they suspect something more serious:
Frequent choking or gasping for air:
If a baby consistently exhibits episodes of choking or gasping for air during sleep, it may indicate an underlying respiratory issue or sleep disorder. This should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out any potential concerns.
Prolonged periods of disrupted sleep:
If a baby consistently has difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or wakes up frequently throughout the night, it may suggest an underlying sleep disorder or discomfort. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help identify the cause of these disruptions and provide appropriate management strategies.
Excessive daytime sleepiness:
If a baby appears excessively drowsy or sleepy during waking hours despite seemingly getting enough sleep at night, it may indicate an underlying medical condition such as sleep apnea. A healthcare professional can evaluate the baby’s symptoms and recommend further assessment if necessary.
Failure to thrive:
If a baby is not gaining weight appropriately, experiencing difficulties with feeding, or showing signs of developmental delays alongside eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. These symptoms could be indicative of an underlying health issue that requires investigation and intervention.
If any of these signs are present or if parents have any concerns about their baby’s health, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
How can parents differentiate between normal developmental patterns of eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep from potential underlying health issues?
Differentiating between normal developmental patterns of eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep and potential underlying health issues can be challenging for parents. However, there are certain factors that can help in making this distinction:
Frequency and duration:
If the eye rolling and rapid breathing episodes occur sporadically and last only a few seconds to a couple of minutes, it is more likely to be within the normal range of development. However, if these behaviors are frequent, prolonged, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it may warrant further evaluation.
Presence of other symptoms:
If the baby exhibits additional worrisome symptoms such as choking, gasping for air, excessive daytime sleepiness, or failure to thrive alongside eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep, it may indicate an underlying health issue. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the cause of these symptoms.
Impact on overall well-being:
If the baby appears otherwise healthy, happy, and is meeting developmental milestones despite occasional eye rolling and rapid breathing during sleep, it is more likely to be within the normal range. However, if these behaviors significantly impact the baby’s overall well-being or disrupt their ability to get adequate restful sleep, seeking medical advice may be beneficial.
Ultimately, if parents have any concerns about their baby’s eye rolling or rapid breathing during sleep or suspect an underlying health issue may be present, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional for proper assessment and guidance.
In conclusion, baby eye rolling and rapid breathing while sleeping is a common and typically harmless occurrence. However, if parents notice any concerning symptoms or changes in their baby’s behavior, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and peace of mind.
Why is my baby breathing hard and fast when sleeping?
It is common for newborn babies to breathe rapidly, even while sleeping. They may also have long pauses between breaths or make noises while breathing. These characteristics are due to the physiology of a baby, as they have smaller lungs, weaker muscles, and primarily breathe through their noses.
Is it normal for babies to breathe erratically while sleeping?
Even babies who are healthy and born at full term may experience periods of periodic breathing. These episodes commonly occur during deep sleep but can also occur during light sleep or when the baby is awake. It is important to note that a baby experiencing periodic breathing will always resume regular breathing on their own.
Is it normal for babies to sleep with eyes open or seizures?
In many cases, nocturnal lagophthalmos in infants is actually a natural occurrence and does not have a medical cause. Sleeping with partially open eyes does not typically result in any symptoms. Although the medical term may sound complex, it is actually quite common among both adults and babies.
Why does my baby twitch and eyes roll while sleeping?
Researchers at UI suggest that the jerky movements infants make during REM sleep are connected to their sensorimotor development. These twitches help stimulate various circuits in the developing brain and enable newborns to learn about their limbs and their capabilities.
What does RSV breathing look like?
Babies experiencing severe RSV will exhibit rapid, shallow breathing. This can be recognized by the chest appearing to cave in between and under the ribs (chest wall retractions), the nostrils widening with each breath (nasal flaring), and unusually fast breathing.
What does respiratory distress look like in infants?
Signs and symptoms of the condition include making a grunting sound with each breath, changes in the color of the lips, fingers, and toes, widening of the nostrils when breathing, and the skin over the breastbone and ribs retracting during breathing.
Emily Mcmelon is a highly skilled and accomplished writer specializing in the field of pediatrics. With a deep passion for children’s health, she has dedicated her career to creating informative and engaging content that helps parents and caregivers navigate the complex world of pediatric care.